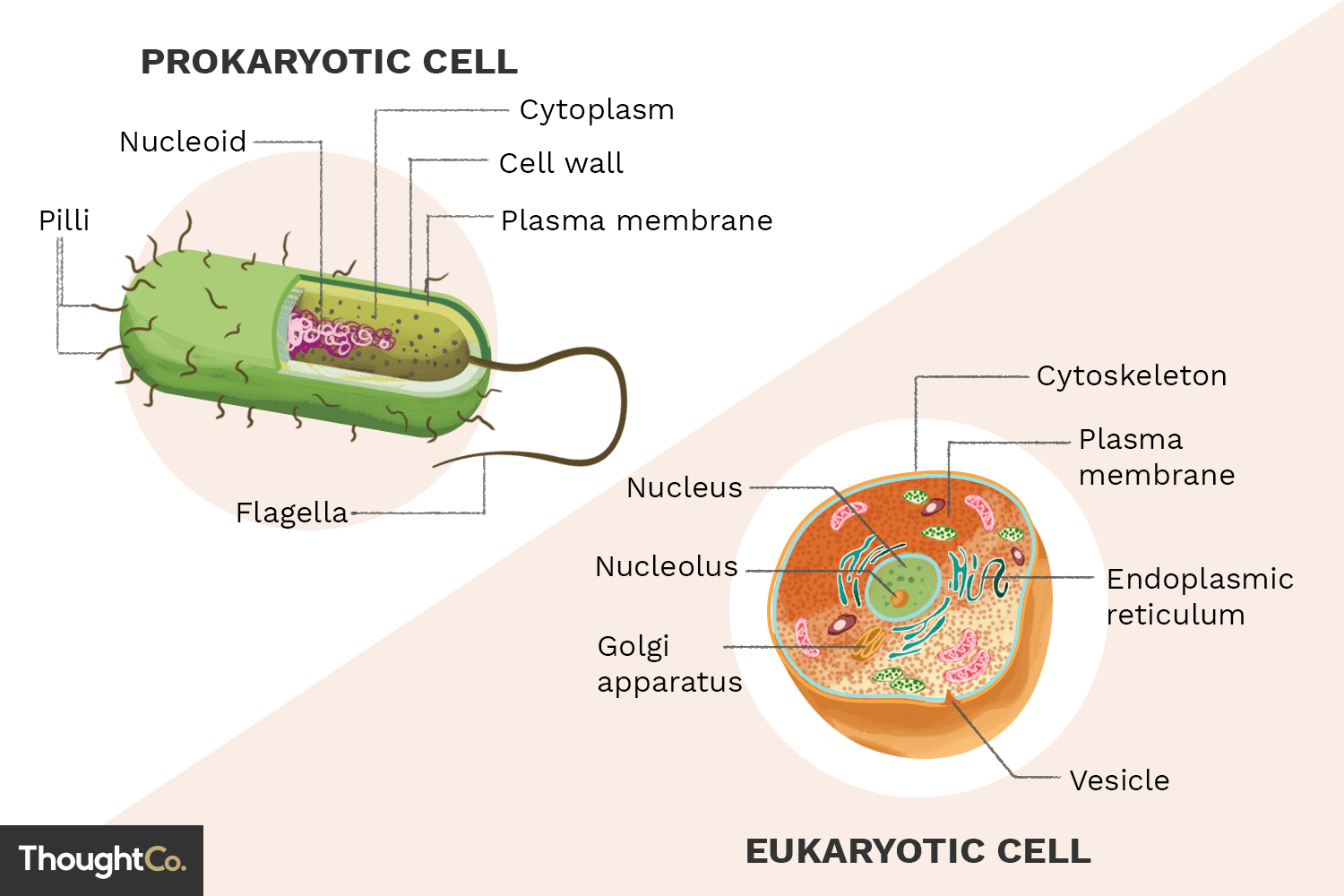
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that one has a nucleus and the other one doesn't. More specifically, prokaryotic cells have no nucleus and eukaryotic ones do. The nucleus is also where majority of a cell's DNA gets stored. In eukaryotic cells this DNA is called nuclear DNA while in prokaryotic cells the DNA gets stored at a region of the cytoplasm also known as nucleoid. Another difference between the two is that eukaryotic cells make both unicellular and multicellular organisms (humans), while prokaryotic cells make only unicellular organisms (bacteria). Lastly, prokaryotic cells have one membrane while eukaryotic have two.
Cellular organelles and their functions
The cellular organelles are:
- The Nucleus, which serves to store the cell's DNA.
- The Nucleolous, which is inside the nucleus and creates ribosomes. (There may be more than one)
- The Cytoplasm, which contains the other organelles of the cell inside it.
- The Cytosol, which holds water and nutrients.
- The Cytoskeleton, which offers structure and support to the cell.
- The Ribosomes, which create protein.
- The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, which creates proteins for the endomembrane system.
- The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, which cleans the cell.
- The Golgi Apparatus, which categorizes and decides where various proteins should go in the body.
- The Mitochondria, which produce energy.
- The Lysosomes, which get rid of unwanted products of the cell.
- The Peroxisome, which play an important role in the metabolism.
- The Vacuoles, which store water and nutrients.
- The Vesicles, which transfer material inside the cell to where it should go.
- The Cell Membrane, which controls what chemicals enter and exit the cell, seperating it from its environment.
- The Cell Wall, which has a protective role.
- The Large Central Vacuole, which stores water.
- The Chloroplasts, which use the process of photosynthesis to feed the cell.
Sources
- libre texts/Bookshelves/Human Biology/Cells and Cell Organelles
- Khan Academy/Cellular organelles and structure (article)