Central Nervous System |
The central nervous system controls all the functions of our body. It consists mainly of the brain and the spinal cord. Both of these are surrounded by three protective membranes, the meninges. In between of the two inside meniges (subarachnoid space) lies the cerebrospinal fluid, which protects and supports the brain and the spinal cord.
The spinal cord is a thin, almost cylindrical, stele of nervous tissue, protected by the spinal canal. It starts at the level of the foramen magnum (hole in the center of the occipital bone) and it ends at the level of the second lumbar vertebrae (lumbar region). At the region of the nape and at the lumbar region, the spinal cord becomes thicker.
From the spinal cord sprout thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves. The spinal cord contains centers of reflexes and it connects the brain with the spinal nerves.
While the central region of the spinal cord is made of grey matter (neuron bodies), the outside is made of white matter (axons).
The brain is the biggest and most complicated part of the nervous system. It consists of neurons which receive, analyze, and transfer stimuli. Some specialised regions, the brain centers, are responsible for memories, control of muscle movements, perception, and emotions. The brain can be anatomically divided into three regions; the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem.
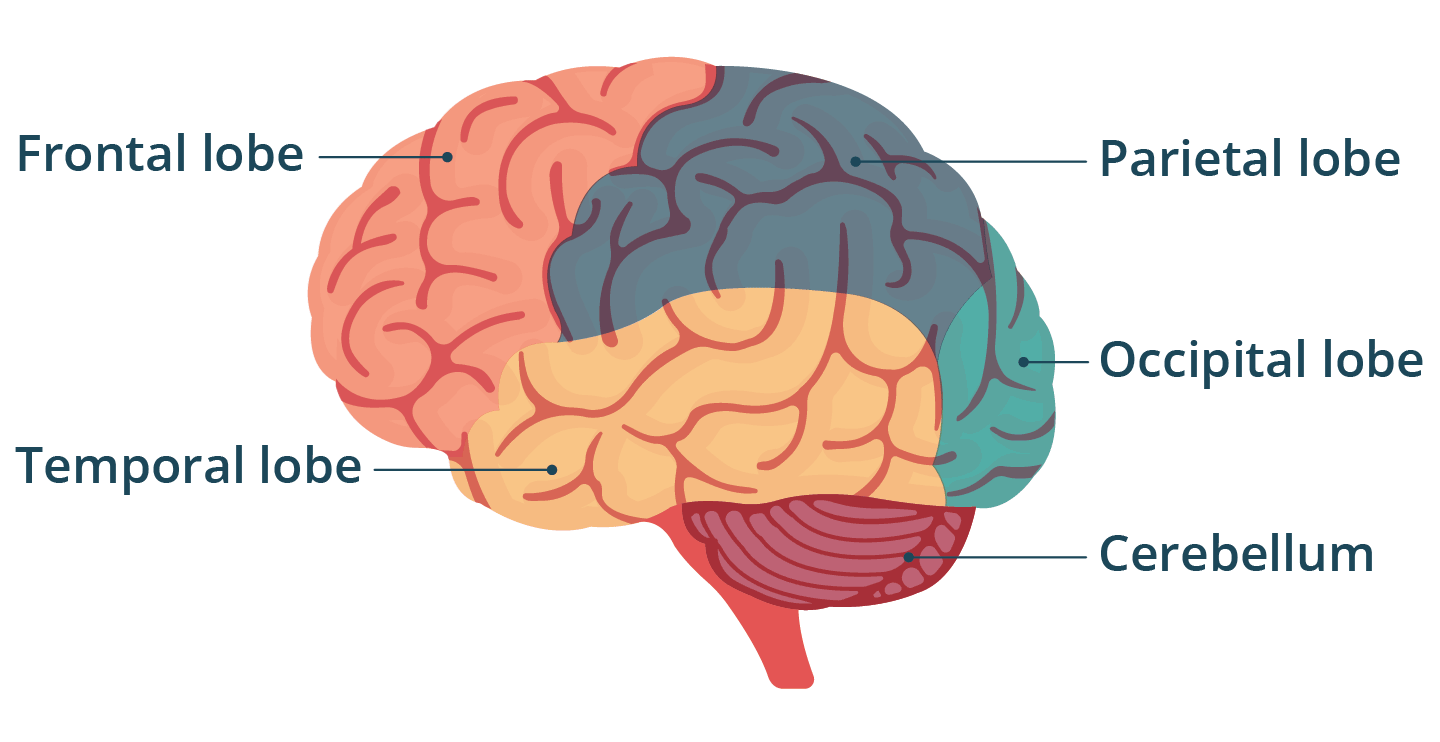
The most important part of the brain is the cerebrum. Above it is a thin layer, the cerebral cortex.The cerebral cortex is the only region of the central nervous system which is responsible for conscious functions. A sulcus (a furrow) is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus, which gives the brain its characteristic foldings. The larger sulci are called fissures. The longitudinal fissure (also called interhemispheric fissure, cerebral fissure, median longitudinal fissure, great longitudinal fissure) splits the brain into two halves called brain hemispheres. The two brain hemispheres get connected at their base by the corpus callosum, made of nerve endings. Other fissures divide each hemisphere in lobes. These are named after the cranial bone which they are above, and are the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe, and the occipital lobe.
Contrary to the spinal cord, the central region of the cerebrum is made of white matter (bundles of nerve endings), and the outside layer of the cerebrum, the cerebral cortex, is made of grey matter (neuron bodies).
The cerebellum consists of two hemispheres, which get connected by a structure called the vermis.
Like the cerebrum, the center of the cerebellum is made of white matter, and the outside layer of the cerebellum, the cerebellar cortex, is made of grey matter.
The cerebellum controls the movements of the skeletal muscles, the body's stability, and the mantaining of the muscle tone.
The brainstem connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. Its most important operational regions are the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata.