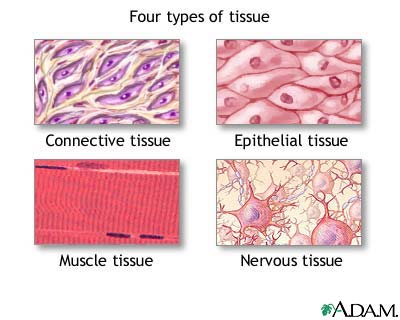
Epithelial tissue
The epithilial tissue consists of cells closely connected with each other. These create surfaces which cover the body on the outside, or on the inside, in cavities. Epithelial cells come in a lot of different shapes and sizes. In fact, the ones which make up the capillary wall are always flat.
The role of the epithelial tissue is mainly protective. Its functions are to get rid of mucus and dust, to allow the absorbance of substances, and to help the body produce and exude products. Occasionally, the cells of the epithelial tissue may produce or exude a product, in which case they are using a gland to do so. A gland might be constituted of many cells (salivary glands) or just one (like the mucosal cells of the gastrointestinal tract).
Glands can be seperated into three categories:
- Exocrine glands, which exude their products either to the outside or to the inside in cavities.
- Endocrine glands, which exude their products straight to the blood.
- Mixed glands, which contain both exocrine and endocrine parts.
Connective tissue
The connective tissue consists of cells embedded in amorphous, intercellular substance. This substance may contain two kinds of protein fibrils (very small fibers). One is collagen, which makes the substance more durable and flexible. The other is elastin, which gives additional flexibility to the intercellular substance.
The connective tissue serves to connect structures with one another, but also protect and support the body.
There are four categories the connective tissue can be split into based on its characteristics:
- connective tissue: loose connective tissue (can be found primarily in the skin, its intercellular substance contains elastin and collagen fibers), dense fibrous connective tissue (can be found in the ligaments of the joints and in the tendons that connect skeletal muscles to bones, its intercellular substance consists of collagen fibrils in bunches), adipose tissue (special type of loose connective tissue whose cells store fat)
- cartilage tissue: Cartilage tissue is solid but also flexible. Its cells, the chondroblasts, are located in cavities of intercellular substance. This type of tissue can be found in articular cartilage, in the wing of our ears, in the intervertebral discs, etc.
- osseous tissue: Osseous tissue, which can be found in bones, consists of really hard intercellular substance, which contains collagen fibrils and salts. In cavities of osseous tissue exist osteocytes (bone cells).
- blood: Blood is widely thought to be a special type of connective tissue. It is made of three different cell categories (red blood vessels, white blood vessels, and blood platelets). The osseous tissue's intecellular substance is in liquid form and constitutes the blood plasma. There is an entire unit devoted to blood. For more information click
Muscle tissue:
The muscle tissue consists of cells, the muscle fibers, which have the ability to contract, allowing us to perform different movements.
There are three types of muscle tissue:
- Skeletal muscle tissue: can be found in skeletal muscles, consists of long cylindrical muscle fibers which bear lines, contracts by our will.
- Cardiac muscle tisue(myokardium): can be found in the walls of the heart, its muscle fibers are cylindrical and bear lines, doesn't contract by our own will.
- Smooth muscle tissue: can be found on walls of vessels or on the walls of the gastrointestinal tract, consists of fusiform muscle fibers without lines, doesn't contract by our will.
Nervous tissue
The nervous tissue consists of neurons, also called nerve cells, and glial cells, also called neuroglia or simply glia. Neurons are specialised in the producing and transfering of nerve impulses (electrical charges which travel along the membrane of a neuron). On the other side, the glial cells feed, support, and isolate the neurons.
So, as we can see, a tissue may contain various types of cells, but these have to participate in the same function.
Sources
- Biology book of A Lyceum from the Greek Ministry of education
- libre texts/Learning Objects/Worksheets/Biology Tutorials/Tissues